 eParts
for
AutoCAD Architecture 2007 - 2009
eParts
for
AutoCAD Architecture 2007 - 2009Doors Installation Guide
IMPERIAL - RESIDENTIAL
Contents:
Greetings
---- Installing eParts ---- Using
eParts ----
Modifying eParts ----
Relocating a Catalog ----
Reporting Problems
|
|
 eParts
for
AutoCAD Architecture 2007 - 2009 eParts
for
AutoCAD Architecture 2007 - 2009Doors Installation Guide IMPERIAL - RESIDENTIAL
Contents: |
| 1Greetings | .1-1 INSTALLATION GUIDE | ||||||||
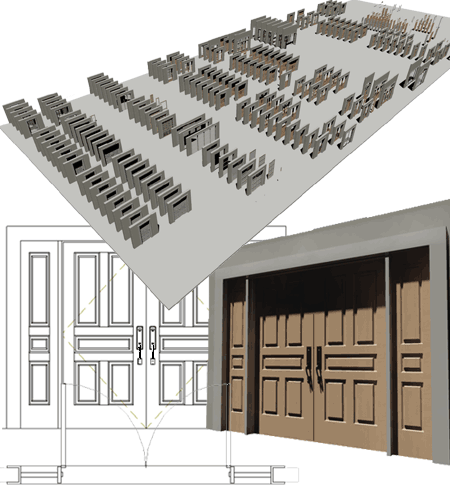
| Introduction Thank you for purchasing an eParts product from ARCHIdigm. eParts are comprised of collections of specific Object Types or Categories such as Refrigerators, Furniture and Street Lights. Many of these Objects come from our eKit products that offer a whole suite of tools for specific tasks such as creating kitchen or bathroom designs. Most eParts have been created as Multi-View Blocks (MvBlocks) consisting of Model, Plan and Mask components. Elevation Views are derived from the Model. Masks are for Plan use only and have been created by using a custom AecPolygon Style with a masking effect that can be turned on or off at any time. Some MvBlocks have a higher level of detail under the High Detail than the Low Detail. Some eParts, like Street Lights, have also been configured to repeat at intervals that you can control by working with the custom Curtain Wall Styles. Most of the Door Styles in this eParts product have been created by using custom Door/Window Assembly Styles as Blocks that replace the default Door Panel in Door Styles. Though this is a little complicated, it offers a new level of flexibility in the look and design of Door Panels. |
 |
||||||||
| 2Installing eParts | 2-1 INSTALLATION GUIDE | ||||||||
Downloading and Installing the Files
Note:
|
|
||||||||
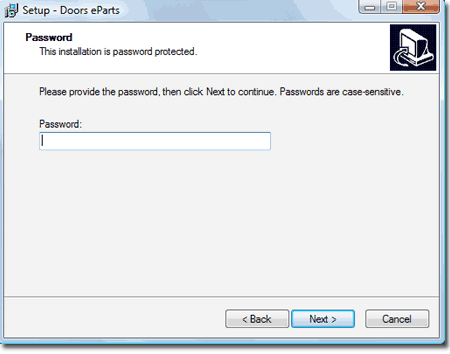
| Provide
Installation Password The password for your product is located in your purchase confirmation e-mail under the heading, "keycode". Use this password to complete the installation. |
 |
||||||||
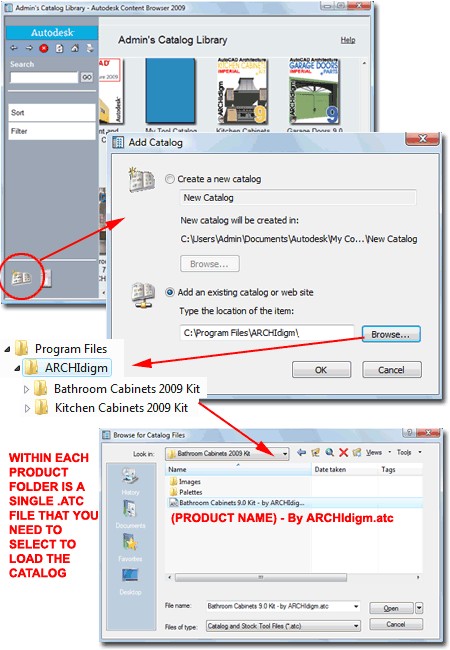
Add Catalog
STEP 2: Once you have Opened the catalog file, you should find that you have a new Catalog Library with a Graphic Image that you can Select to access all of the Tools and Tool Palettes discussed below.
|
 |
||||||||
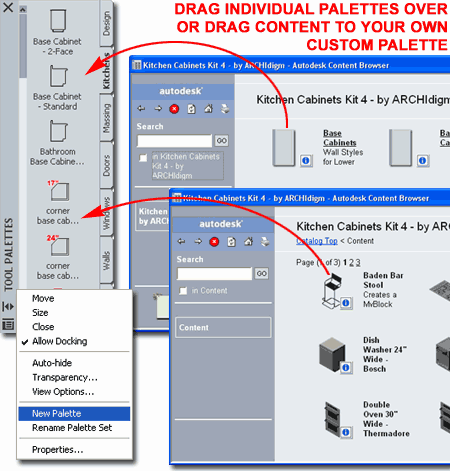
Add Tool
Palette, Category and Tools
STEP 3: Tip: You can use the Ctrl+A keystroke technique to highlight all tool icons under a Catalog Category or you can Select off in a corner and use the Selection Window to highlight a group. The Shift and Ctrl keys work to assist in Selecting items just as they do in Explorer. |
 |
||||||||
| 3Using Doors 9 eParts | 3-1 INSTALLATION GUIDE | ||||||||
| Adding
Doors There are two Door Types in this package: Door Objects and Door/Window Assembly Objects. Adding both Door Types is just like adding native ACA Objects. The Door Objects are based on standard ACA Styles but with a variety of modifications like hardware and trim. Included with this package are Door Styles that come straight from the stock ACA library and should behave just like stock content (trim and hardware has been added). The Door/Window Assembly (DWA) Objects were designed to provide solutions for entry systems with sidelights and transom windows. The two main features of the Doors in this package are trim, hardware and custom panels. For the most part everything else will work like native ACA Objects. The more you know about how to work with ACA Objects, the more you will be able to modify the Doors in this package. I have placed all of the customized objects in the core library file to make it easier to make personal adjustments or even build entirely new Door designs. Note: |
 |
||||||||
| Door Objects | |||||||||
|
Working with Door Objects When you add a regular Door Object, not a DWA, you should find that it behaves much like regular ACA Door Objects. However, there are some significant and important differences that you need to know about if you wish to make changes to the results you get. The Trim, for example sits on the outside of any Wall you Anchor to by virtue of the "Auto-adjust to Width of Wall" Door Style setting. The Trim is also controlled by custom Structural Member Styles, an Inside and an Outside one, that use custom "MemberShape" profiles. For many of the Door Styles, the Panel itself is actually a Block that replaces the default Panel component with a highly customized DWA Object Style that includes things like stiles, rails and so forth. And finally, there are knobs, levers, pull-handles and more that have been added as Blocks. |
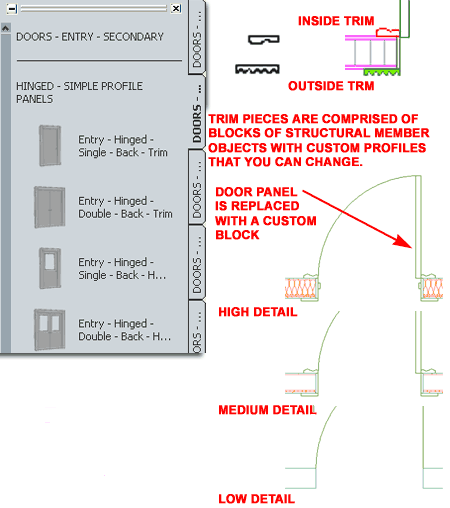 |
||||||||
| Simple Door Panel
Breakdown Though this package is primarily based on complex door panels, there are numerous Door Styles based on simple Profile Definition Styles. The use of Profiles is consistent with the stock Door Styles that come with ACA. In the illustration to the right I show a simple glazed entry door with muntins (2x4). Because the native Muntin Block, inside the Display Properties of Door Styles, always maintains scalar proportions this is a superior solution to using a Block replacement for the Panel. For cases such as this one, we chose to use Profiles but in cases where we wanted more sophisticated paneling, we chose to use Door/Window Assembly Styles as Door Panel replacements (see below).
|
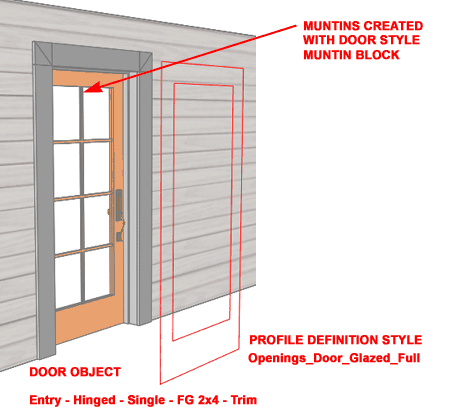 |
||||||||
| Complex
Door Panel Breakdown The default Door Panel Component of Door Styles has very limited options for higher levels of detail so this Component has been turned off and replaced with a custom Door/Window Assembly Style. Essentially, it works like this: 1) a custom DWA style was created to represent a Door Panel. 2) the custom DWA was drawn to a specific size and turned into a Block 3) a Door Style was created where the default Panel Component was replaced with the Block from #2 above. This means that if you want to modify the Door Panel, you can insert the Block for that Panel and "Refedit" (Edit the Block in Place) it or go straight to the Door/Window Style dialog and work through it. To change the Materials, for example, it would much better to go to the Door/Window Style. In the illustration to the right I show how the names of these components have been structured to help find matches. |
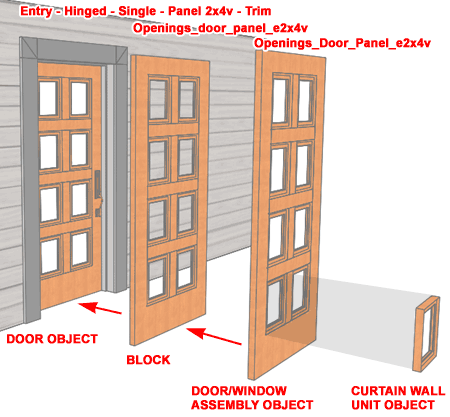 |
||||||||
| Door Panel
Display Properties In the illustration to the right I show how the default Door Panel Component is replaced with the DWA Style Block. Under the Display Properties, the Door Panel Display Component has been turned Off but in its place, is a custom Block added under the "Other" tab.
Note: |
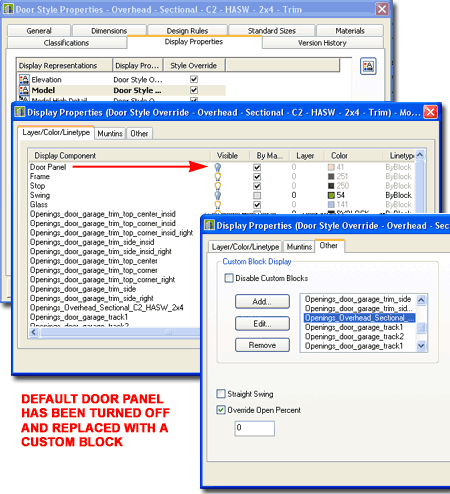 |
||||||||
Modifying
Trim on Door and Window Objects
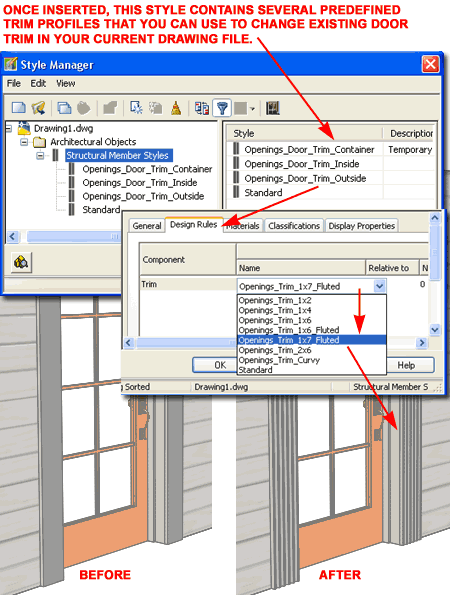
Door Styles labeled with "Trim" as a suffix in their Style names, use Structural Member Styles for inside and outside Trim. The trim is actually comprised of a series of Blocks of Columns attached to the outside edges of the Door Frames. By using this technique, you can easily change the shape of the Trim by using the "MemberStyle" command to access the dialog box illustrated to the right. On the "DOORS - TRIM, TOOLS, HARDWARE, ETC." Palette, you will find a button labeled "Modify Trim Profile" and when you pick on this button, it will insert a collection of predefined Member Shapes (see discussion below). Once the custom Member Shapes have been imported into your drawing, you can use the "MemberStyle" command to access the Trim Styles for inside and outside positions and change the shapes under the "Design Rules" tab, "Name" drop-down list, to other trim shape names.
Note: |
 |
||||||||
|
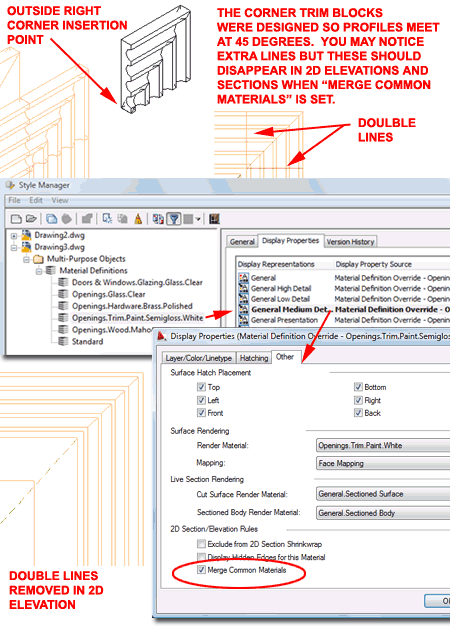
Understanding Trim Corners The corner trim for Door and Window Objects consists of a special Block of a Structural Member that bends by 90 degrees. In order to get the Structural member to work properly, a tiny amount of straight length had to be added along the head and jamb directions This results in a set of double lines where the head and jamb trim meet the corner trim. The lines will disappear when using ACA's 2D Elevation and Section tools as long as the Material Definition Style for the trim is set to "Merge Common Materials" under the "General Medium Detail" Display Representation (see images to the right). The corner trim was designed to accept Profiles for things like flutes. However, should you want to create a unique corner trim solution, you can replace or substitute your own design for our default one. Each corner has a Block name; for Doors the names are as follows: "Openings_door_trim_top_corner_right" ,"Openings_door_trim_top_corner", "Openings_door_trim_top_corner_insid_right" and "Openings_door_trim_top_corner_insid". You can, for example, create a model of a medallion and replace any of these Blocks with that medallion design. Be aware, however, that our corners use the same Profiles that the other trim components use and will thus grow, contract and/or adjust shape to match. Custom designs, unless they use the same principle, will remain static in size and shape.
|
 |
||||||||
Creating
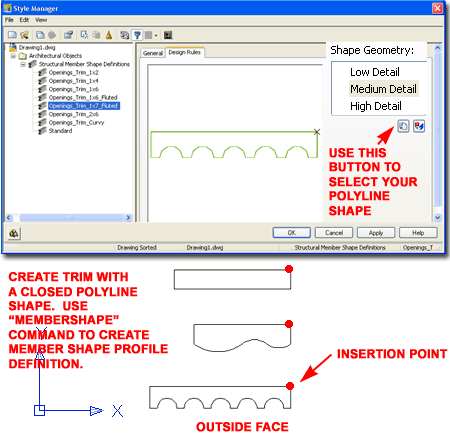
Custom Trim Shapes for Door and Window Objects
In the illustration to the right I show three example Trim Profile Shapes that were created with Polylines. To create your own shape, simply draw a closed Polyline form, to scale, and use the "MemberShape" command to activate the dialog illustrated to the right. The Structural Member Shape Definitions dialog shows three Display Representations under the Shape Geometry category. Use the "Specify Rings for ..." button to Select your custom Polyline shape for each Display Representation. For advanced users, you can actually specify different Polyline shapes for different Display Representations. The insertion point for your custom Polyline shape is always the upper right corner, as illustrated, and the outside face is always along the x-axis pointing towards the negative "Y" direction. |
 |
||||||||
Adding
Trim Manually - Part 1
The custom trim solution provided in this product only work on rectangular shaped Door and Window Object Styles (DWA Styles use another trim solution). This means that if you want trim on unusual shapes and you don't want to use a DWA, you will need to add the trim manually. In the illustration to the right I show what happens when you change the default "Rectangular" shape of one of our modified Door Styles to something like "Peak Pentagon". There was no way for us to make the trim automatically follow the shape so, as you can see, it remains in the original rectangular form. In a scenario like this, you have two choices: you can remove the trim Blocks from the Door Style or you can import one of the numerous DWA Door Styles that don't have the trim - type "DoorStyle" and Open "C:\Program Files\ARCHIdigm\Doors 2009 eParts\Doors eParts - (Imperial).dwg" to import Door Styles with a "DWA" prefix. To Remove the default Trim Blocks, use the Door Style Properties dialog to access the "Elevation", "Model" and "Model High Detail" Display Representations. Use the Other tab to Remove every Block with the term "trim". When you have removed the Trim Blocks from these three Display Representations, uncheck the "Plan" and "Plan High Detail" Display Representation Overrides to remove the Trim Blocks from those two Plan Display Representations. Once you have a Door or Window Object without the Trim Blocks, you can manually add the trim to whatever shape you want. |
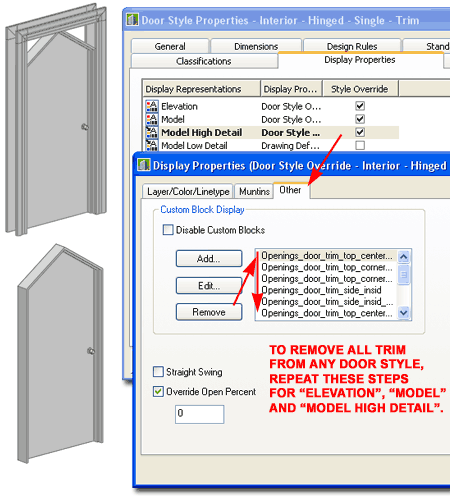 |
||||||||
Adding
Trim Manually - Part 2
Trim Styles, which are actually Member Styles, can be imported into any ACA drawing by using the Insert Interior Trim Tool or Insert Exterior Trim Tool. If you have already added one of our doors with trim, then you already have at least one of the two trim styles. To add trim manually to a Door, Window or other Opening, draw a Polyline along the inside frame edge. I typically do this along the outside of my Doors or Windows. Doors don't need a sill and Windows should have a separate Polyline for sills because those typically use a different Profile shape. The direction of the Polyline, clockwise versus counter-clockwise, only matters if the Profile is asymmetrical (such as the example to the right). After you have drawn the Polyline shape, use the "ColumnConvert" command to convert the Polyline into a Structural Member. On the "Convert to Column" dialog, do not use the "One Member Per Polyline Segment" option. The default Structural Member will be a large square but you can change that on the Properties Palette to "Openings_Door_Trim_Inside" or "Openings_Door_Trim_Outside", for example. If you Zoom into one corner of the new trim, you are likely to find that it requires some Justification modifications and/or Mirroring. If you draw the Polyline in the right direction for the trim profile, you won't need to change the Justification Once the trim is located in the proper position relative to your Door or Window, use the Anchor Trim to Door or Window Tool to hook the trim to the Door or Window. This action will connect the trim to the primary Object so if you Move it, the trim moves as well. Anchoring does not change the shape and size of the trim so if you change the Door or Window size, you will have to modify the trim manually as well. |
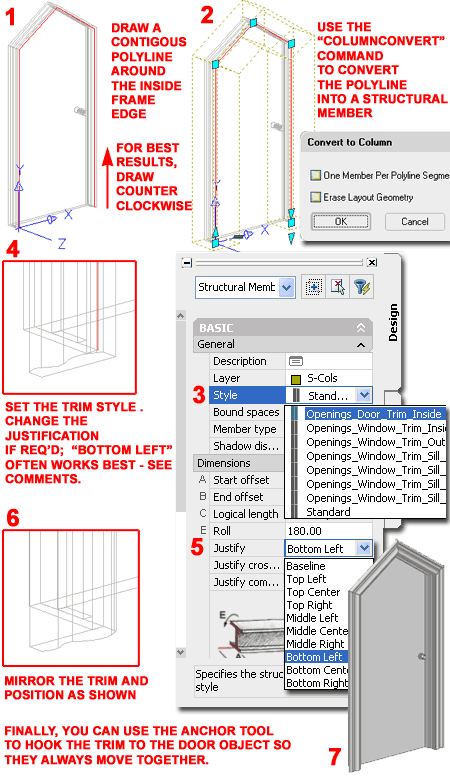 |
||||||||
Adding
Trim Manually - Part 3 - Windows
For manually add trim to a Window Object, use the Insert Window Trim tool to import the default rectangular Window Trim Block. This action will introduce the MemberStyles needed for your work and you should be able to use the Sill portion of the imported style. On the inside edge of your window jamb and head, draw a contiguous Polyline as shown. As with the instructions for the Door Object above, use the "ColumnConvert" command to turn the Polyline shape into a Structural Member Shape. Then, change the Member to "Openings_Window_Trim_Outside" or "Openings_Window_Trim_Inside". Move the Sill portion of the original Trim Block into position and Grip Stretch the Sill to match you window width (see illustration, right, for how to Stretch two Grips simultaneously). When you have the two trim components in place, use the Anchor tool to Select both trim components and Anchor them to your Window Object. Anchoring does not change the shape and size of the trim so if you change the Window size or shape, you will have to modify the trim manually as well. These steps can be repeated for the other side of the Window. However, you can also just Mirror the trim and use the Properties Palette to assign the appropriate Member Style.
|
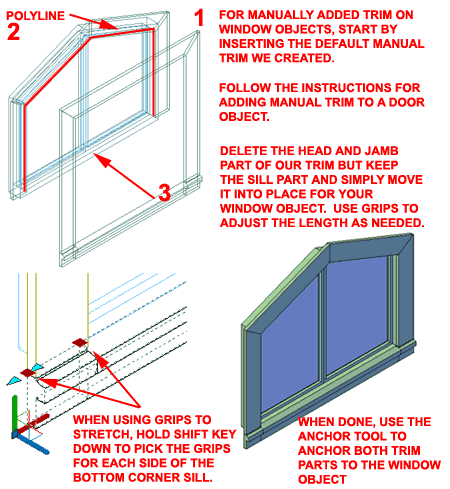 |
||||||||
| Door/Window Assembly Objects | |||||||||
| Working
with Door/Window Assembly Objects When you add one of our customized DWA Objects, such as those for Entry Systems, you should find that they behave much like regular ACA DWA Objects. However, there is one one major difference and that has to do with our efforts to provide a solution for trim. DWA's use a Frame component for Jambs, Heads and Sills and since these accept custom Profile shapes, we created a default "C" shape to produce a trim-like effect. Unlike the trim we used for our Door Objects, this profile solution is somewhat static and does not automatically adjust to varying Wall Thicknesses. Once you develop the skills to modify the Profiles and a few DWA Style settings, you should find that the limitations are not that dreadful.
Note: The "FacetDev" setting can be used to improve the appearance of curved surfaces. Set to a lower number to improve things like arched top doors. The default value is 1/2. I often use 1/10 - 1/100 depending on the size of the file and the detail needed. |
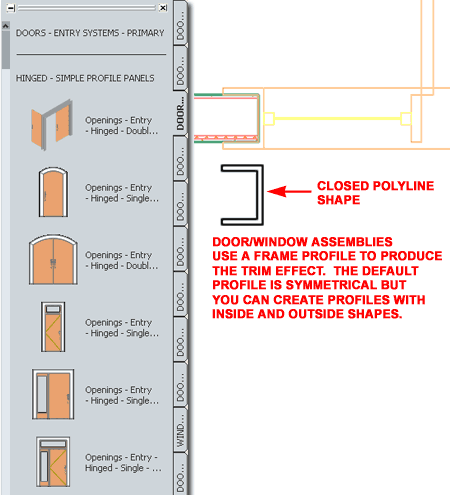 |
||||||||
|
Door/Window Assembly Panel Breakdown If you have reviewed the breakdown of our Door Objects in this guide, you will be familiar with a portion of the complexity involved in how our Door/Window Assemblies have been put together. The Entry Systems, such as the one illustrated to the right, are fairly complicated but this complexity was necessary in order to provide design flexibility and relative scalar accuracy; a Sidelight Panel, for example, should match the main Door Panels. Essentially an Entry System is just a Frame with Mullions and Cells that have been assigned a variety of custom Styles such as Doors and Curtain Wall Units. The Door Styles are duplicates of the ones with trim but lack both the trim and Frames (the Style names always have a prefix of "DWA"). For Sidelights and Transoms we used custom Curtain Wall Units (CWU) because they maintain relative scalar proportions unlike Blocks. DWA Styles available in this package should be seen as templates for your own creations. It is fairly easy to take a default DWA configuration and change Doors and Sidelights (for more, see below). |
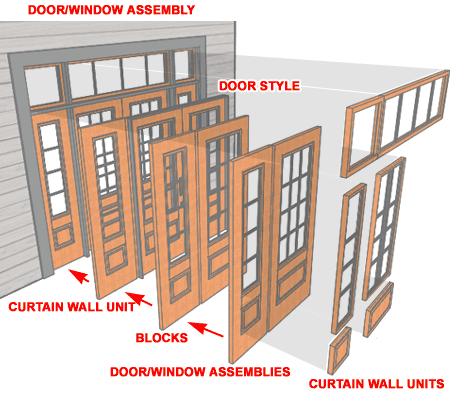 |
||||||||
| Modifying
Door and Sidelight Infill Assignments The easiest way to change the Door and/or Sidelight Styles in a default DWA Entry System is to also insert the DWA Entry System that has the configurations you desire. Once you have the primary DWA Entry System you want and the Door and/or Sidelight Styles, all you have to do is Modify the Infill settings of the primary DWA Style. Illustrated to the right I show an example of how I have added the "Openings - Entry - Hinged - Double - 2 Sidelight - 3 Transom A - Trim" DWA Style with the default plain solid doors and glazed sidelights. To give myself access to the Doors and Sidelights I really want, I show that I have added the "Openings - Entry - Hinged - Double - 2 Sidelight - Panel 2x4v - Trim" DWA Style off to the side. This action imports the Door Style and Sidelight (CWU) Style designed for use in DWA's. After importing the Styles that I wanted, I show that I have activated the "Door/Window Assembly Style Properties" dialog by Selecting the outer Frame of the Entry System and using the "Edit Door/Window Assembly Style..." context menu option. To illustrate how Doors, Sidelights and Transoms are set as Cells in the DWA, I show how the Bottom Cell Assignment has another Cell Assignment set to "Doors Solid". For some of the more complicated Entry Door Systems, I have set a default for "Doors Full Glazed" to provide quick access to glazed doors and you can just use the drop-down list to change the assignment. However, if you want to use a completely different Door Style, go straight to the Infills category and highlight the "Door", "Doors" or "Doors Solid" (depending upon the type of DWA) Infill and set a different Door Style under the Styles list. For Sidelights and Transoms, the Style list should automatically go to the "Curtain Wall Unit Styles" section of the Style list. Be sure to confirm this or you might end up with Doors in your Sidelight or Transom locations. Note: |
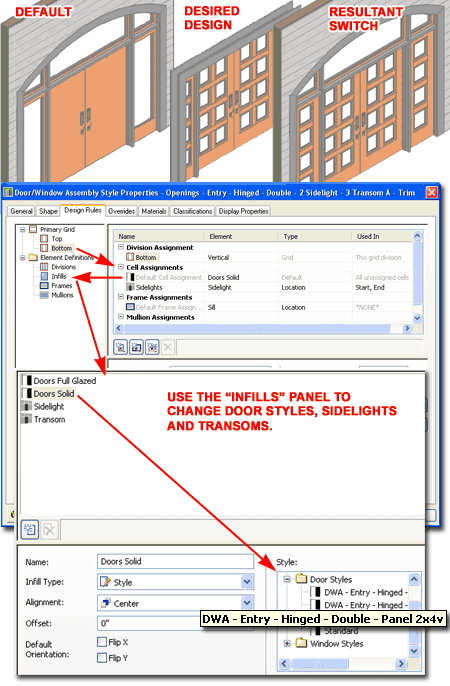 |
||||||||
| Creating
Custom Trim Shapes for Door/Window Assembly Objects Entry System DWA's use Profile Definition Styles to produce a trim-like appearance and the one major drawback to this solution is that the Profiles don't automatically adjust to varying Wall Widths. In the illustration to the right I show an example of how the default Profile Definition Style, named "Openings_DWA_Trim_Jamb", isn't deep enough to match the Wall Object it has been placed in. Because the trim has been drawn as 1" thick on each side of the Profile, it does protrude out beyond the Wall edges and may never be noticed as a problem. However, it isn't that difficult to fix and knowing how to fix it will allow you to create more customized trim solutions. The default "Openings_DWA_Trim_Jamb" Profile can be inserted using the "Profile" command with the "P" option. You can use the default shape to assist you in creating a new one or you can simply draw a Closed Polyline shape. Use the diagram to the right as your guide for drawing the Jamb and Head Profile. For this example, all I need to do is Stretch the Depth to match the Width of my Wall.
Once you have a new or modified Profile, Select the DWA Object that you want to apply this Profile to and use the Door/Window Assembly Style Properties dialog to access the Frames category. Illustrated to the right I show how our Entry System DWA's use the same Profile Definition Style name for the Head and the Jambs (Sills are not used but could be by advanced users). Width, Depth, X-offset and Profile Name all need to match the values you provided for your custom Profile shape. Note: |
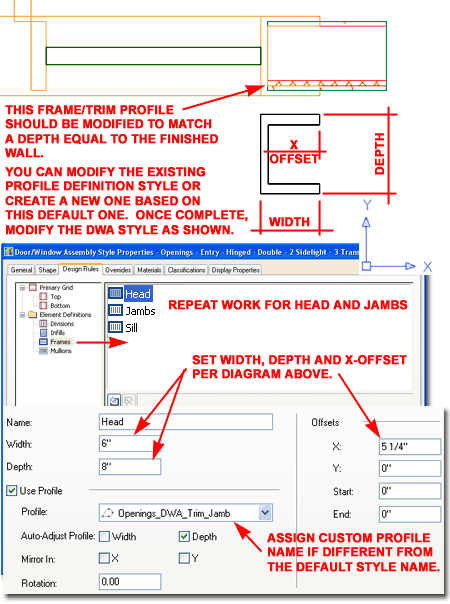 Note: |
||||||||
| Material
Assignments One unfortunate cost of all the customization we did to native ACA Objects in this package, is that modifications to things like Material Assignments, is far more difficult. A complex panel entry door, for example, is comprised of custom Curtain Wall Units, a Door/Window Assembly Style, Mass Elements (for Hardware) and one or two Structural Member Styles (for exterior and interior trim). On the flip-side, however, you can change the material of all exterior door trim with a couple of clicks. For some it may appear as a daunting task to understand how all of the Objects in this product have been nested into each other. If you find that are perplexed and simply cannot find the core or root Object for something you want to change, I recommend that you use a blank ACA file and insert the Door Object into it so you don't have to scroll up and down lists full of information that has nothing to do with the Doors. We have done our best to use names that match from primary object style all of way down to Curtain Wall Unit panels. You can also Open any of the Library files to view a matrix of the Object hierarchy - C:\Program Files\ARCHIdigm\Doors 2009 eParts\. Note about Sidelights: |
Material Assignments for Door Objects Trim - use "MemberStyle" Material Assignments for Door/Window Assembly Objects Trim - use "DoorWinAssemblyStyle" Material Assignments for Window Objects Trim - use "MemberStyle" |
||||||||
| 2D Projected
Elevation/Section Results with Missing Trim In the illustration to the right I show an example of how trim may disappear in 2D Projected Elevations and Sections. The cause of this is may be due to conflicting or overly complicated trim components. In some cases, for example, I have experienced this problem due to inadvertently leaving both the true corner and straight corner trim components on. If you experience this problem, the best solution I have come up with thus far is to simply change the Material for the problematic trim components. As illustrated, lower right, use the Structural Member Style dialog to access the trim components and then change the Material to one that does not use the "merge" option.
|
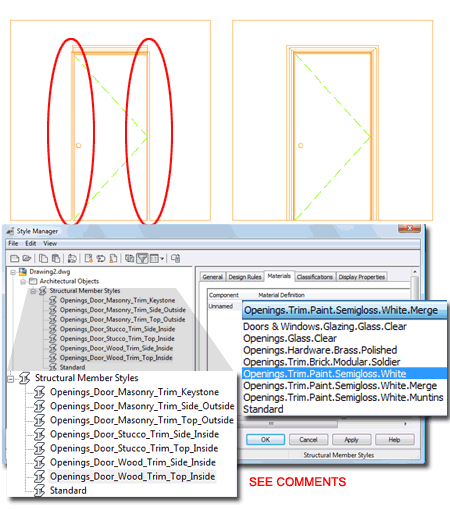 |
||||||||
Template Files and Display Configurations
All ePart Objects have been optimized for
work using the AutoCAD Architecture 2007 - 2009 "Aec model
Illustrated to the right is an example of how the three primary Display Representations, Low, Medium and High Detail, affect ePart Objects. Most ePart Objects include an AecPolygon Style set to Mask background information. This mask can be turned off if desired.
Low Detail
Medium Detail
High Detail Note: |
|
||||||||
| 4Modifying eParts | 4-1 INSTALLATION GUIDE | ||||||||
Multi-View
Block Anatomy
Most ePart Objects involve a complicated set of regular Blocks that have been assembled into a Multi-View Block. The complexity varies and may never be something you will have to think about but if you ever have a need to change one of these Objects, you will need to understand how they have been assembled. The most important thing that you need to understand about MvBlocks is that there is always a duplicate Block of the 3D Model Representation. By looking under the Model Display Representation on the Multi-View Block Definition Properties dialog, you can find the name of this matching 3D Model Block. By inserting this Block you can use Refedit to make changes to things like Material Assignments, Height, Width and so forth. Multi-View Blocks also provide the option to set different Blocks for Top (Plan) Views and these may even be different for Low, Medium and High Detail Display Representations. A feature of our eParts Objects is the use of custom AecPolygon Styles that act as Masks to hide Objects below. If these mask blocks produce undesirable results, you can turn off the masking feature - see comments below. |
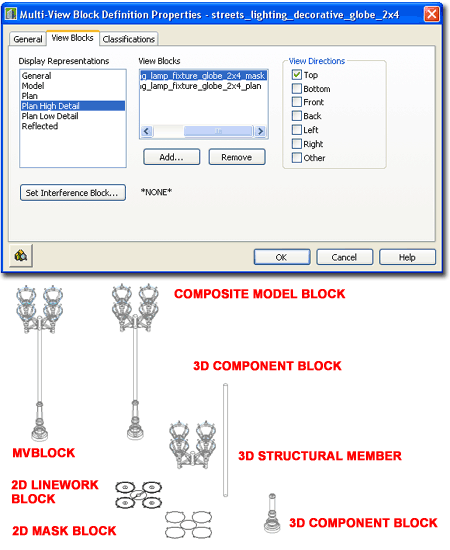 |
||||||||
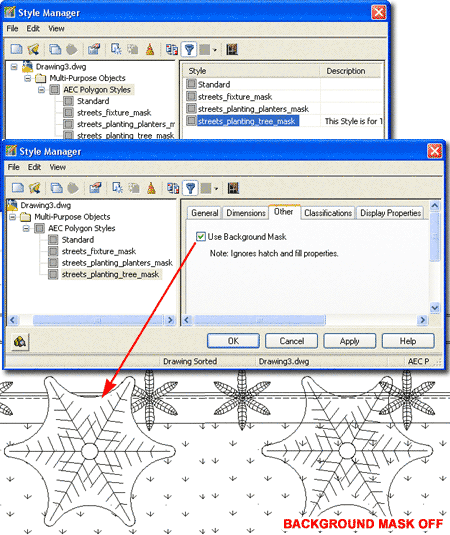
Masks, AecPolygons and MvBlocks
Most ePart Objects include a Masking Block as part of their structure. These Masking Block have been created by making a Block of an AecPolygon Object set to a custom Style where the "Use Background Mask" feature has been activated. By typing "AecPolygonStyle" on the command line, you should see a list of Styles with the word "mask" as suffix. By Editing any of these Styles and unchecking the "Use Background Mask" feature found under the "Other" tab you can remove the masking behavior - see illustration right. Mask Blocks may produce undesirable results when printing from Model Space due to the Black Background but this is not a problem when printing from Paper Space Layouts. The "DrawOrder" command can be used to move Mask Blocks up or down in the display stack. Note: |
 |
||||||||
Materials and
Mass Elements
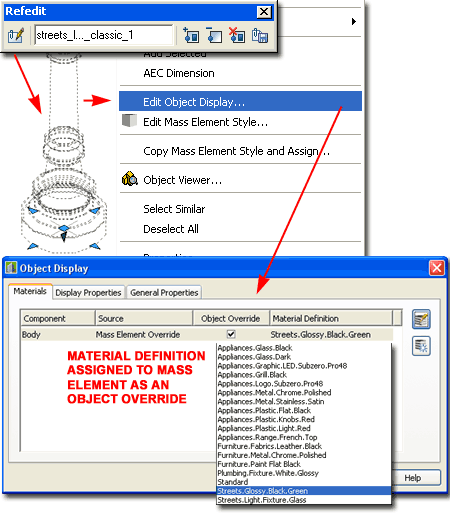
Most ePart Objects incorporate Mass Elements as a means of providing a 3D Model that will accept Material Definition Assignments. In other cases native Object Styles, such as Structural Members, Curtain Walls and Railings have been used whenever feasible and their Material Definition Assignments are managed by the Object Style. For Mass Elements, however, the Objects have typically been assigned to one custom Mass Element Style and Material Assignments set as Object Display Overrides. For Objects such as this, you can use the Refedit command to access the Edit Object Display... context menu option to change the Material Definition Override under the "Materials" tab - see illustration to the right. Keep in mind that an MvBlocks contains one or more regular Blocks so in order to access the actual 3D Model information you need to Insert the 3D Model Block, typically denoted by an "m" suffix. Once you have inserted the 3D Model Block, you can use the Refedit command to access the contents inside the Block in a way that will ripple back to the MvBlock once you save the changes. If you Open the eParts source file you will find that most of the 3D Model Blocks have been inserted for you so you can more easily identify them and even change them in this source file if you feel the need. Note: |
 |
||||||||
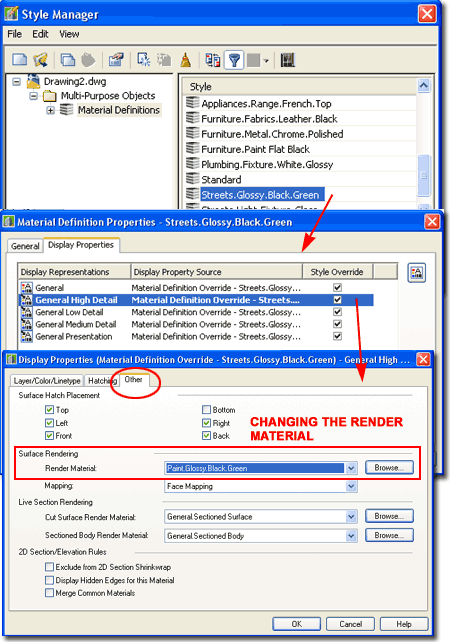
| Materials - an
alternative approach to changing the Rendering Material If you are in a hurry and don't have the patience to change Material Definition Assignments remember that you can always change the Material Definition Style itself. For example, just because a Material Definition Style is named "Streets.Glossy.Black.Green" does not mean that you can't change the actual Rendering Material to a Glossy Red.
|
 |
||||||||
| 5Relocating a Catalog | |||||||||
| Overview about
Moving a Catalog AutoCAD Architecture's Content Catalog offers a Publish tool that assists users with the management of Catalog and drawing file paths. This tool works well with ACA items such as Object Styles and MvBlocks but ignores regular AutoCAD objects like Blocks. Our eKits and eParts often include tools set to insert regular AutoCAD Blocks. These tools have to be fixed manually if you intend to move a catalog to a server or other location. |
|||||||||
|
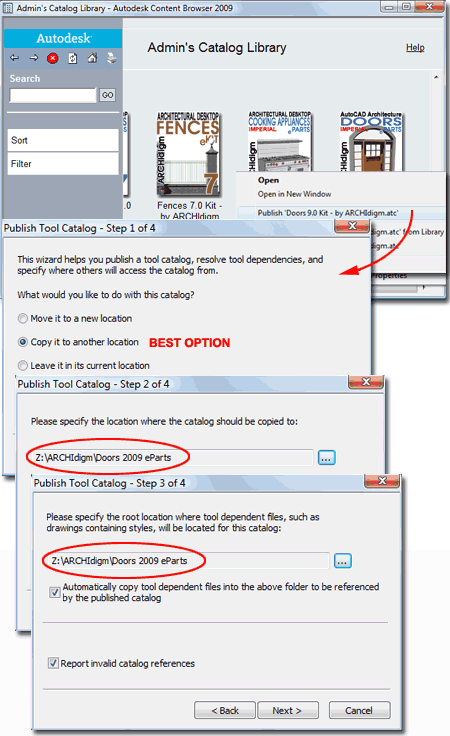
Customizing Installation Paths Note: Be sure to create your folder structure for the new location prior to using the Publish tool. I recommend that you use the same folder name for this product as was used for the default installation. Though this product has been configured for installation under the "C:\Program Files\ARCHIdigm\Doors 2009 eParts" path, you can alter this after you have installed and loaded it in your Content Browser. From the Content Browser, Select the "Doors 9.0 ePart - by ARCHIdigm" Catalog icon, right-click and Select the "Publish 'Doors 9.0 ePart - by ARCHIdigm'" from the context menu - as illustrated right. On the Publish Tool Catalog - Step 1 of 4 dialog box, you can use the Move or Copy options to direct this product to a new folder location on your local drive or on a Network Server. I highly recommend that you create a new folder location that uses the same primary folder name as the one we assigned for the original installation; e.g., "X:\my server\my ACA content\Doors 2009 eParts". On the Publish Tool Catalog - Step 2 of 4 dialog box, use the ellipses (...) button to specify a new location for the catalog. On the Publish Tool Catalog - Step 3 of 4 dialog box, use the same location path as the one you previously specified since that is where all of the "tool dependant files" need to go and check both "reference" related checkboxes. The final step completes the task and provides a report on any errors. You should now find a new Tool Catalog. If you used the Copy option the new Catalog will have "Copy" in the title but you can rename it as you see fit. After testing the tools, you may want to delete the original Catalog and Folder on your local drive. |
 |
||||||||
| Publishing
Report If you opted to use the "Report Invalid Catalog References" checkbox on the "Publish Tool Catalog - Step 3 of 4" dialog box (see illustration above), you may find errors for items the Publish tool did not Copy. Make a note of these items and simply Copy them manually. In the illustration to the right I show that for some reason Render Materials, the image files, are not copied. |
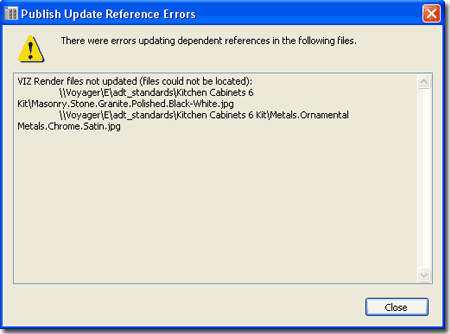 |
||||||||
| Understanding
Relocated Folders and Files Content Catalogs are basically Tool Palettes stored in a single Browser. The information within the Tool Palettes is stored in XML coded files with the extension ".atc". Because the files are written in XML code, you can edit these with an XML editor or something as simple as Windows' Notepad. Illustrated to the right I show an example of how a relocated Content Catalog may appear under a mapped drive labeled as "Z". If you have more than one of our products, you may want to create a primary folder, like "ARCHIdigm" and then create sub-folders to match the default product folder names. After using the Copy option under Publish in the Content Browser, all folder and files should have been copied as illustrated to the right. The primary product folder should only contain one .atc file that serves as the main Catalog file. This file should not require any modifications. There should also be one or more folders labeled "Images", "Palettes" and possibly "Categories" (depending on the product). Within the Palettes folder you should find files with the ".atc" extension and these are the actual Tool Palettes. These may require editing based upon the information listed below. Within the Categories folder, if it exists, you should find another sub-folder labeled "Palettes". The files within this Palette folder may require editing based upon the information listed below. Doors 9.0 eParts Palette files requiring
manual editing: Categories / Palettes |
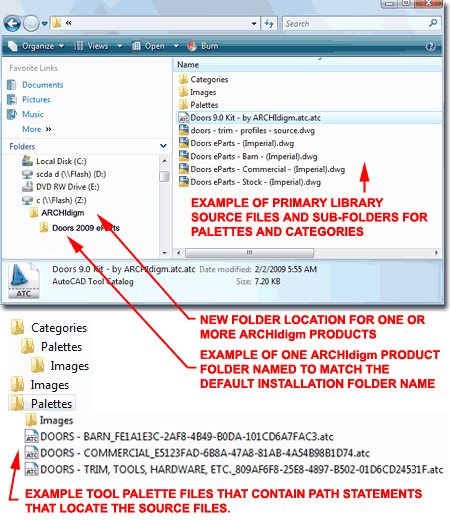 |
||||||||
|
Customizing
Installation Paths Manually Note: Be sure to do this work with AutoCAD Architecture shut down. If it is running it can overwrite any editing you may have done. Based on the ".atc" files listed above, find each in your new location and use Notepad to edit them. In each file use the Replace command found under the Edit pull-down menu and input the following information for the "Find what" field: "C:\Program Files\ARCHIdigm\Doors 2009 eParts". For the "Replace with" field, specify your new path location. In the example listed above, my Replace with field would look like this: "Z:\ARCHIdigm\Doors 2009 eParts" After modifying one of the .atc files in this fashion, Save it and repeat the work for each of the .atc files listed above. |
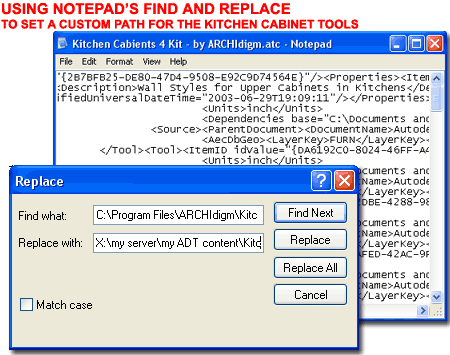 |
||||||||
| Test your
editing To confirm that your editing was successful, go to the new Doors 9.0 eParts Catalog and open the "DOORS - TRIM, TOOLS, HARDWARE, ETC." Palette. If you can insert any of the Trim Objects and Door Knobs, your editing worked out perfectly. If you receive an error, something must have gone wrong with the Find and Replace work. At this point you may need to contact someone at ARCHIdigm - see e-mail address below. |
|||||||||
| 6Reporting Problems | 6-1 INSTALLATION GUIDE | ||||||||
|
Responding Let us know what you would like to see improved. |
|
© Copyright 2009 ARCHIdigm. All rights reserved.